The series is an important device in measuring and monitoring current in power systems, especially in industrial and automation applications. Proper selection and use of converters will help protect equipment, ensure safety and optimal performance of the electrical system.
1. The basic information about current tranformer
The current transformer's English name is Current Transformer. The current transformer symbol is CT. is an electronic device used to measure the level of current in an electrical circuit. As a converter, the CT receives the input current signal and converts it into a signal suitable for reading or processing. The main use of the current transformer is to reduce the magnitude of the current from a high level to a low level, so that other reading or measuring devices can handle it.
Current transformer, also known as current transformer, is an indispensable device in the power monitoring and measurement system.
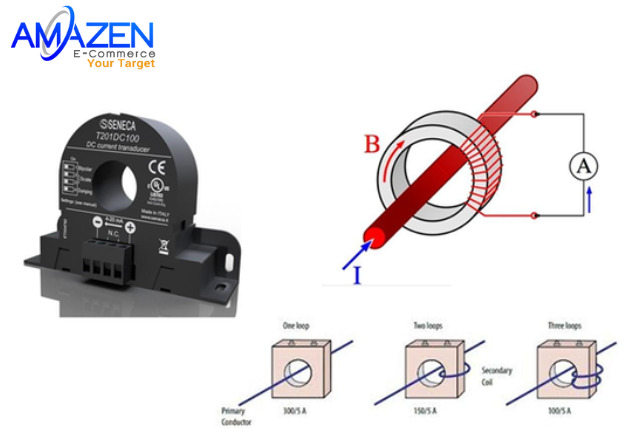
For example, we often see 100/5A, 330/5A, 100/1A or 500/1A current CTs, etc. These parameters mean that when we pass 100A or 300A current through the current CT, we get 5A. , 1A.
Current tranformer signals
- Current Transformer (CT symbol), is a type of "voltage measurement tool" designed to create an alternating current with an intensity proportional to the initial current intensity.
- Current transformer is the English name of the current transformer. With our calling, they can be: current transformer, current CT, CT current transformer, current sensor, current transformer, ...

2. Structure of current tranformer
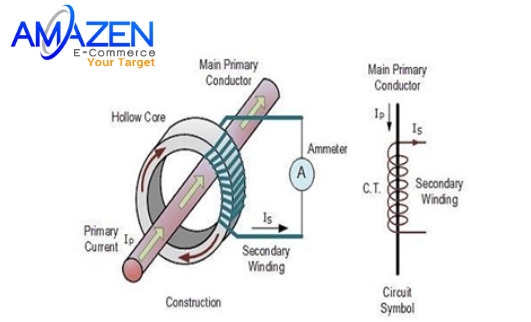
A current transformer is a device used to transmit and convert electricity to other devices, consisting of many turns of wire wrapped around a magnetic iron frame. Current transformers can consist of one or more turns of wire depending on the design. The structure of a conventional current transformer includes the following main parts:
- Primary Current: Primary current: Primary current is the current connected beyond the center of the current transformer. This line will have a voltage current of several hundred amps or more.
- Secondary Winding: The secondary coil is the output coil in the current transformer. They are ordinary electrical wires wound around, close together at the wall of the current transformer core. The secondary coil is responsible for producing signals of 5A, 1A,...
- Hollow Core: Is the most important part of the measurement current transformer. The core is made of magnetic material, designed with the right shape and size to create the magnetic field effect needed to measure current.
- Ammeter : Measure voltage mmeter
Looking at the picture above, we can see that the structure of the current transformer simply consists of a steel core wrapped around copper wire.
The steel core of the current transformer is used to conduct the main magnetic flux of the machine; Made from good magnetic conductive materials such as electrical engineering steel. The steel core is made into a circle where the secondary winding is placed.

In addition, an indispensable component of the current transformer is the outer plastic shell. The outer shell is made of insulating plastic to protect the secondary winding; ensure operator safety.
3. The current tranformer in operating priciples
The operating principle of a current transformer is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. When alternating current flows through a wire, it creates a changing magnetic field around the wire. This magnetic field will induce the secondary coil of the current transformer, creating an induced current in the coil.
A current transformer has two basic operating modes: open-circuit mode and short-circuit mode.
- Open-circuit secondary mode: When the secondary circuit is open, a high induced voltage will appear on the secondary side, which can be dangerous for people and secondary devices. To prevent saturation in the magnetic circuit, a linear current transformer, also known as a current transformer with an air gap, is sometimes used.
- Short-circuit mode of the primary current: The secondary side has a load Z2Z_2Z2; the ratio between the short-circuit primary current and the rated current is called the current transformer multiple. When this multiple is large, the CT error increases, and this error also depends on the secondary current or load. For protection circuits, the CT current multiple must be chosen such that the error is kept below 10%.
Since the current transformer’s current ratio is inversely proportional to the number of turns in the winding, the transformation ratio can be adjusted by changing the number of turns in either the primary or secondary winding.
4. The current tranformer roles
Today, human life relies heavily on electrical energy, so current transformers are widely used in systems for monitoring and measuring electrical energy of various devices such as: electricity meters, wattmeters, protection relays, etc.
A current transformer provides a standard secondary current, ensuring that even if this current reaches its maximum value, it will remain within the safe operating range of an ammeter.
Current transformers are essential devices in electrical monitoring and measurement systems. Simply put, a current transformer is an electrical device used to convert high-value currents into standard currents of 5A or 1A, providing a safe voltage for measurement, control, and protection circuits.
In addition to the traditional current transformers that operate on electromagnetic principles, there are now newer types of current transformers used for ultra-high voltage grids to reduce insulation costs compared to conventional current transformers.

The block-type current transformer is used in various cable types and busbars of the main electrical circuit. It is similar to a primary coil but has only a single turn of wire. These transformers are completely isolated from the high-voltage source operating in the circuit and are always connected to the load current in electrical equipment.
There are numerous devices that apply and utilize current transformers, with typical examples including wattmeters, power factor meters, electricity meters, protection relays, or even the release coil in the magnetic circuit breaker mechanism...
5. Why we use current tranformenr
The use of current transformers offers many important benefits. Below are some reasons why you should use current transformers for measurement:
- Protect devices and system: Current transformers help detect the current in the circuit and provide information to protection devices such as circuit breakers (MCBs) or protection relays. This helps prevent overcurrent incidents and protects the system from damage.
- Measure and control: Current transformers allow for the measurement and control of current in electrical systems. With continuous monitoring, you can track performance and optimize the operation of electrical equipment.
- Save energy: By monitoring the current, you can identify issues related to inefficient energy consumption and find ways to improve. This helps save energy and reduce operational costs.
- Safety for user: The use of current transformers reduces the risk of electrical accidents by providing accurate information about the current in the circuit. This helps prevent electric shocks and other safety hazards.
6. How to read "current tranformer" specification
A type of 100/5A current transformer. Simply, when a current with a value of 100A flows in the coil of a current transformer, it will produce a current with a standard value of 5A. In other words, this current transformer will convert a current with a value of 100A into 5A. In addition to the 100/5A current transformer, we also have other types of current transformers such as 150/5A current transformer, 400/5A current transformer, 250/5A current transformer, 800/5A current transformer, 600/5A current transformer, 1000/5A current transformer. .
This is some "current tranformer" popularity appear in market

7. Current tranformer type
It has 2 way to discern current tranformer
7.1 Following functions
7.1.1 Measure current tranformer
For measurement current transformers (MCT), the secondary current will reach saturation when the primary current exceeds the rated value. This type of current transformer is always used for energy meters.
7.1.1 Protection current tranformer
For protection current transformers (PCT), the secondary current will far exceed the rated value when a fault occurs on the primary side (such as a short circuit on the power line). Protection current transformers are always used for protection relays.
Protection current transformers typically come in 5PX and 10PX types. In this notation, 5 or 10 refers to the error margin of 5% or 10% of the current transformer. "P" stands for "Protection," and "X" represents the multiple of the primary current exceeding the rated value (usually 10 or 20 times).
Important Note: Users should always be cautious to avoid using current transformers for the wrong purpose: do not use measurement current transformers for relays and do not use protection current transformers for meters.
7.2 Following the structure
7.2.1 Wound Core Current Transformer
In a wound core current transformer, the primary coil is directly connected to the conductors to measure the current flowing through the circuit. Typically, the current in the secondary coil is entirely dependent on the turns ratio of the current transformer.


7.2.2 Ring-Type Current Transformer
In a ring-type current transformer, there is no primary winding. Instead, the current flowing through the circuit is transmitted directly through the opening or gap in the "ring" of the current transformer.
Currently, some ring-type current transformers are designed with an additional "split pin," which allows the opening or gap in the transformer to be opened, installed, and closed without the need to interrupt the circuit.

Open-core ring-type current transformers are detachable types. They are mainly used to measure current in locations where direct installation is difficult. This type is necessary to measure current or voltage in such cases.

7.2.4 Block-Type Current Transformer
his is one of the common types of current transformers used today, typically applied in cables and busbars of the main electrical circuits. It is similar to the primary coil but with only a single turn of wire.
They are completely isolated from the high-voltage source operating within the circuit and are always connected to the load current in electrical equipment. Today, to directly measure the current or voltage in a circuit or electrical panel, handheld clamp-type current transformers are commonly used. They are mainly applied for monitoring or checking if current is flowing through the circuit.

8. Current tranformer in industry
In industry, machinery and equipment are connected to form a complex system to achieve optimal automation. To ensure the system operates efficiently, the devices must have superior functions and be compatible with each other, especially in terms of signal transmission. These signals must be standardized so that the control devices can communicate and function accurately.
Current transformers are no exception. Today, there are many types, models, and, notably, different signal types of current transformers. Each type of signal is designed to work with specific control devices such as PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces), or ammeters. Choosing the appropriate signal type between devices ensures that the system operates accurately and efficiently.
8.1 Current tranformer 4-20mA
The Analog Current Transformer (CT) is a type of current transformer with output signals of 4-20mA or 0-10VDC. It is used for motor protection relays or to read the primary current value, and can be directly connected to a PLC.

Typically, when we want to remotely monitor the current via an analog signal, we often need to use a signal converter to change the 0-5A signal to 4-20mA or 0-10VDC. However, with a current transformer that has a 4-20mA output, we can use the output directly for monitoring, which significantly reduces costs.
8.2 Current tranformer 1600/5A
The 1600/5A Low-voltage Cast Epoxy Current Transformer (CT) is a ring-shaped measuring current transformer used to convert high alternating current into a smaller value suitable for measuring instruments like ammeters, wattmeters, or energy meters.
8.3 Current tranformer 500/5A
This type of current transformer is medium-range, commonly used for controlling currents from 0 to 500 amperes. It is often found in plastic manufacturing plants, CNC machines, or transformer stations.
8.4 Current tranformer 125/5A
Similarly, the 125/5A Current Transformer is also quite popular, particularly in systems with low power and currents ranging from 0 to 125 amperes.
9. Current Transformer Operation Guide
Biến dòng sơ cấp chỉ có 2 dây ngõ ra loại dòng 5A, 10A. Cách đấu dây biến dòng với đồng hồ hiển thị khá đơn giản. Nhưng có một điều cần lưu ý, là phải chọn loại đồng hồ hiển thị ampe tương đương với biến dòng đang sử dụng
9.1 The way to choose current tranformer
9.1.1 Current tranformer rate
The current transformer ratio is the ratio between the rated primary current and the secondary current. This ratio is usually clearly marked on the current transformer.
In practice, current transformers with a ratio of x / 5 A are commonly used. Most metering devices are compatible with current transformers that have a secondary current rating of 5A. Additionally, for some technical and economic reasons, current transformers with a ratio of x / 1 A are also used when long signal cables need to be run. The line loss when using a 1A current transformer is only 4% of the loss when using a 5A current transformer. However, the measurement accuracy of the device will be slightly lower in this case.

Rated current
To select a current transformer (CT), the first step is to determine the maximum load current that will pass through the transformer. Then, you should choose a current transformer with a value equal to or slightly higher than the actual current value.
Rated current refers to the value of the primary and secondary current of the current transformer, and it is always clearly marked on the transformer. Standard primary rated current values (excluding those with accuracy classes 0.2S and 0.5S) are: 10 – 12.5 – 15 – 20 – 25 – 30 – 40 – 50 – 60 – 75 A, along with their multiples. The standard secondary rated currents are 1A and 5A, with the 5A version being the most commonly produced.
To ensure accurate measurements, we always recommend that customers use a current transformer with a primary rated current slightly higher than the maximum current (In) of the system.
Simple example: If your maximum load current is 450A, you should choose a current transformer with a rating of 500A.
If your load current is less than or equal to 300A, then an analog current transformer is the best option for you.
9.1.2 Power current
The rated power of a current transformer is understood as the maximum power the transformer can handle without causing errors that exceed the permissible limits.
When selecting an appropriate rated power, attention should be paid to the following factors: losses in metering devices (if multiple devices are connected), cable length, and cable cross-sectional area. The longer the cable and the smaller the cross-section, the lower the losses. Therefore, it is important to choose a current transformer with sufficient rated power to accommodate all these losses.
It is necessary to choose a current transformer with rated power close to that of the system's wiring and the metering devices on the secondary side. If the power rating of the current transformer is too low, the transformer may be damaged during a short circuit in the system. If the power rating of the transformer is too high, it will reduce the accuracy of the metering.
Accurancy levels
Current transformers are typically classified into different accuracy classes, and users need to choose the appropriate one based on their intended use and budget.
The standard accuracy classes include: 0.1; 0.2; 0.5; 1; 3; 5; 0.1S; 0.2S; and 0.5S. These accuracy classes indicate the percentage (%) deviation in value and phase shift between the actual current and the secondary current.
The accuracy class of a current transformer is also related to the load current. If the load current is too low compared to the rated current of the transformer, the accuracy will decrease. Refer to the table below:

9.2 The way to wire current tranformer 3 pha
For three-phase currents, we need to use specialized three-phase current measuring devices. Typically, three-phase currents in industrial plants have high power levels, which can range from 10,000 to 20,000 amperes. These types of current transformers generally do not convert the signal directly from amperes to volts. This means that when they are installed on the wiring of a three-phase motor with a current ranging from 0-10,000A, they will convert this current into a voltage signal with a measurement range of 0-10V.

To measure the signal, we use a signal converter to transform the 0-10V signal into an Analog 4-20mA signal or Modbus, making it easier to connect with PLCs, controllers, or display units as shown in the diagram.
9.3 Current tranformer instructional video
10. The current tranformer types in business
10.1 Current tranformer Lightstar

10.2 Current tranformer GIC

Closing remarks
If you need further information or technical advice, feel free to contact Amazen through:
Hotline: 0934 399 068 - Sales: 0938 072 058
Email: amazen@amazen.com.vnWith a highly skilled technical support and sales advisory team, our company is confident in providing our customers with the best shopping experience.
Amazen guarantees that all the inverters we offer are 100% brand new, genuine products, with full certification documents, including CO/CQ and VAT invoices.